Two recent cases of JSE-listed companies reveal the advantages of equity funding over debt funding.
While issuing debt can be more dangerous than issuing equity, it receives more encouragement from shareholders and the regulators. Debt has more upside potential: if a borrower can return more than the costs of funding the debt (return on equity improves) and there is less to be shared with fellow shareholders.
But this upside comes with the extra risk that shareholders will bear should the transactions funded with debt turn out poorly. Any increase in the risk of default will reduce the value of the equity in the firm – perhaps significantly so.
The accounting model of the firm regards equity finance as incurring no charge against earnings. You might think it would help the argument for raising permanent equity capital rather than temporary debt capital. But this is clearly not the case, with the rules and regulations and laws that govern the capital structure of companies. It is also represented in the attitude of shareholders to the issuing of additional equity. They have come to grant ever less discretion to company boards to issue equity. Less so with risky debt.
(Note: I am grateful to Paul Theodosiou for the following explanation of the different treatment of debt and equity capital raising. Paul was until recently non-executive chairman of JSE-listed REIT, Self Storage (SSS), and previously MD of the now de-listed Accucap of which I was the non-executive chairman).
Typically at the AGM, a company will seek two approvals in respect of shares – a general approval to issue shares for cash (which these days is very limited – 5% of shares in issue is the norm) and an approval to place unissued shares under the control of directors (to be utilised for specific transactions that will require shareholder approval). These need 75% approval. So shareholders keep a fairly tight rein on the issue of shares.
Taking on or issuing debt, on the other hand, leaves management with far more discretion. Debt instruments can be listed on the JSE without shareholder approval, and bank debt can be taken on at management’s discretion. The checks and balances are more broad and general when it comes to debt. Firstly, the memorandum of incorporation will normally have a limit of some kind (for REITs, the loan to value ratio limits the amount of debt relative to the value of the assets). If the company is nominally within its self-imposed limits, shareholders have no say. Secondly, the JSE rules provide for transactions to be categorised, and above a certain size relative to market cap, shareholders must be given the right to approve by way of a circular issued and a meeting called. The circular will spell out how much debt and equity will be used to finance the transaction, and here the shareholders will have discretion to vote for or against the deal. If they don’t approve of the company taking on debt, they can vote at this stage. Thirdly, shareholders can reward or punish management for the way they manage the company’s capital structure – but this is a weak control that involves engaging with management in the first instance to try and persuade, and disinvesting if there isn’t a satisfactory response.)
Perhaps the implicit value of the debt shield – taxes saved by expensing interest payments – without regard to the increase in default risk, confuses the issues for investors and regulators. It is better practice however to separate the investment and financing decisions to be made by a firm. The first step is to establish that an investment can be expected to beat its cost of capital, whatever the source of capital, including internally generated cash that could be given back to shareholders for want of profitable opportunities. When this condition is satisfied, the best (risk adjusted) method of funding the investment can be given attention.
The apparent aversion to issuing equity capital to fund potentially profitable investments seems therefore illogical. Or maybe it represents risk-loving rather than risk-averse behaviour. Debt provides potentially more upside for established shareholders and especially managers, who may benefit most from incentives linked to the upside.
Raising additional equity capital from external sources to supplement internal sources of equity capital is what the true growth companies are able to do. And true growth companies do not pay cash dividends, they reinvest them, earning economic value added (EVA) for their shareholders. A smaller share of a larger cake is clearly worth more to all shareholders.
There are two recent JSE cases worthy of notice. Foschini shareholders approved the subscription of an extra R3.95bn of capital on 16 July to add about 20% to the number of shares in issue. By 19 August, the company was worth R25.8bn, or R10.5bn more than its market value on 16 July, or R6.5bn more than the extra capital raised. The higher share price therefore has already more than compensated for the additional shares in issue.
The Foschini Group – market value to 19 August 2020
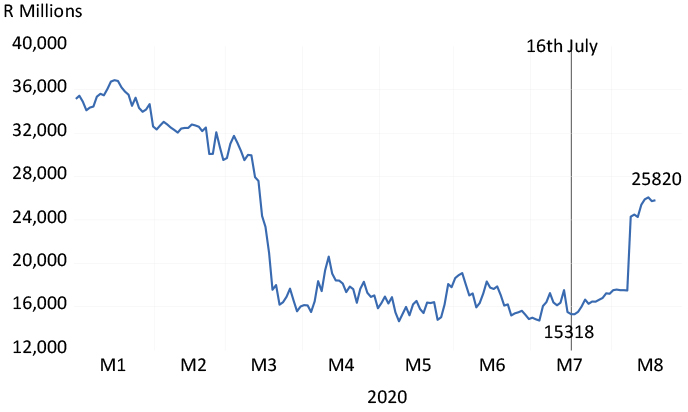
Source: Bloomberg, Investec Wealth & Investment
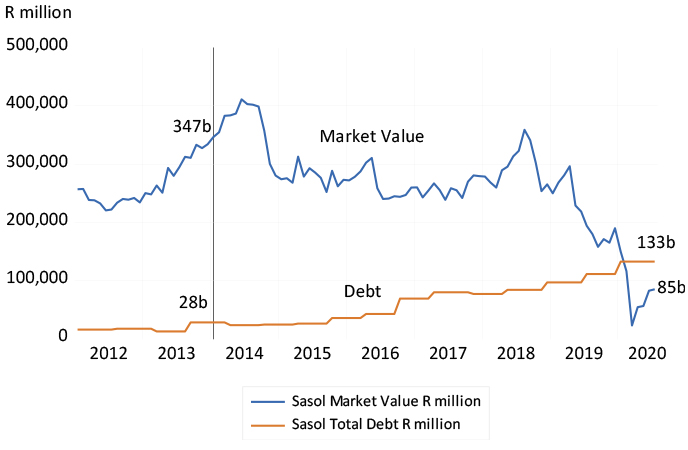
The other example is Sasol, now with a market value of about R87bn, heavily depressed by about R110bn of outstanding debt. The extra debt was mostly incurred funding the Lake Charles refinery that ran far over its planned cost and called for extra debt. Sasol was worth over R400bn in early 2014, with debts then of a mere R28bn. The recent market value, now less than the value of its debts, is clearly being supported by the prospect of asset sales and a potential capital raise.
The company would surely be much stronger had the original investment in Lake Charles been covered more fully by additional equity capital, capital they might have been able to raise with much less dilution. It might also have prevented the new management team from having to sell off what might yet prove to be valuable family silver – assets capable of earning a return above their cost of capital. In this case, a large rights issue could still be justified to bring down the debt to a manageable level and, as with the Foschini increase, the value of its shares by more (proportionately) than the number of extra shares issued.
Sasol – market value and total debt, 2012 to July 2020